GERMANY

Our graduate programs go beyond mainstream thought and practices, fostering intellectual inquiry and creative mastery.
Why Study in Germany ?
Located at the heart of Europe, Germany shares its borders with nine neighboring states. Spanning approximately 357,000 square kilometers, its terrain stretches from the North and Baltic Seas in the north to the majestic Alps in the south. With a population of 83.2 million, Germany stands as the most populous state in the European Union. Notably, over 22 million individuals have roots outside Germany, with 11.8 million being foreign nationals, and more than 10 million holding German citizenship. The primary language spoken across the nation is German, with specific provisions for other languages in different regions such as Upper Sorbian, Lower Sorbian, Low German, Frisian, and Danish.
Germany stands out as an immensely appealing choice for global students, owing to its esteemed education system, renowned universities, and an expansive array of study programs. The country prides itself on providing exceptional research prospects and a strong focus on practical learning, making it an optimal pick for students pursuing top-notch education. Moreover, Germany warmly welcomes international students, offering robust support services like language training and cultural immersion activities. As a result, students from across the globe find Germany an irresistible destination for their academic pursuits.
Studying in Germany offers numerous advantages. Firstly, it boasts world-class institutions like the Technical University of Munich and Heidelberg University, renowned for their diverse study programs encompassing fields like engineering, medicine, and social sciences. Secondly, the German education system prioritizes hands-on learning, equipping students with practical skills for the professional world. Thirdly, Germany’s status as a center for scientific and technological advancements fosters an environment ripe for groundbreaking research and exploration of fresh ideas. Lastly, the affordability factor, with free or low-cost education for both local and international students, alongside various scholarship opportunities, makes studying in Germany financially feasible.
Germany has proudly embraced democracy and a social federation since 1949. The country’s federal structure, rooted in the constitutional legacy of the German Empire and the Weimar Republic, emphasizes regional autonomy. The Basic Law of 1949 underscores the continuity of this federal order, particularly in education, science, and culture. This grants the individual states, known as Länder, substantial responsibility for legislation and administration in these vital domains, ensuring a diverse and community-oriented educational landscape. This federalist approach not only honors Germany’s historical regional diversity but also fosters a vibrant democratic system by encouraging diversity, healthy competition, and locally driven policies.
The educational landscape of the Federal Republic of Germany is characterized by both ideological and social diversity. A significant catalyst shaping the German education system was the collaboration among the Länder through the Standing Conference of the Ministers of Education and Cultural Affairs, established in 1948. The Unification Treaty of 1990 mandated the five Länder in eastern Germany to reform their educational frameworks by mid-1991. This led to the creation of independent Ministries of Education, Cultural Affairs, and Science in these regions. The collaboration among these Länder aimed at establishing a cohesive and comparable foundational structure in the education system, showcasing their commitment to self-coordination within the Federal Republic.”
In summary, Germany’s unique blend of exceptional universities, innovative research prospects, emphasis on practical learning, and cost-effectiveness positions it as an enticing destination for those seeking superior education and a supportive academic milieu.
SCOPE OF CHOOSING GERMANY AS STUDY DESTINATION FOR INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS:
Germany is an exceptional study destination for international students across various fields and levels of education. Here’s the scope and advantages:
1. Education Quality:
World-Class Universities: Germany boasts numerous top-ranked universities renowned for their quality education, research opportunities, and innovative teaching methods.
Cutting-Edge Research: Institutions in Germany are often at the forefront of research in various fields, offering students access to state-of-the-art facilities.
2. Diverse Programs:
Wide Range of Courses: Germany offers a broad spectrum of programs in fields like engineering, natural sciences, humanities, social sciences, business, and arts.
Interdisciplinary Studies: Many programs encourage interdisciplinary approaches, allowing students to explore multiple fields.
3. Affordability:
Low or No Tuition Fees: Most public universities in Germany have either no tuition fees or very low fees for international students, making education affordable compared to other countries.
4. Language Options:
English-Taught Programs: There’s a growing number of programs taught entirely in English, making it more accessible for international students who don’t speak German fluently.
Language Learning Opportunities: Institutions often offer language courses, allowing students to learn German, which can be advantageous for daily life and job prospects.
5. Job Prospects:
Post-Study Work Opportunities: Germany provides opportunities for students to stay and work after graduation through various visa schemes, including an extended job search visa.
Strong Economy: With a robust economy and a need for skilled professionals, there are ample job prospects for graduates.
6. Cultural Experience:
Rich Cultural Heritage: Students can experience Germany’s rich cultural diversity, history, and vibrant cities.
Travel Opportunities: Situated in the heart of Europe, Germany offers easy access to travel across the continent.
7. Requirements and Support:
Admissions: Admission criteria vary between universities and programs but typically require good academic records and, for some programs, language proficiency.
Student Support Services: German universities often provide comprehensive support services for international students, including orientation programs, counseling, and assistance with accommodation.
8. Internship Opportunities:
Internship Programs: Many universities have strong connections with industries, offering students practical experiences through internships, which can enhance employability.
Germany’s focus on innovation, quality education, and emphasis on practical learning makes it an attractive destination for students pursuing various courses at different academic levels. It’s essential for prospective students to research specific programs and universities to find the best fit for their academic and career aspirations.
GERMAN EDUCATION SYSTEM
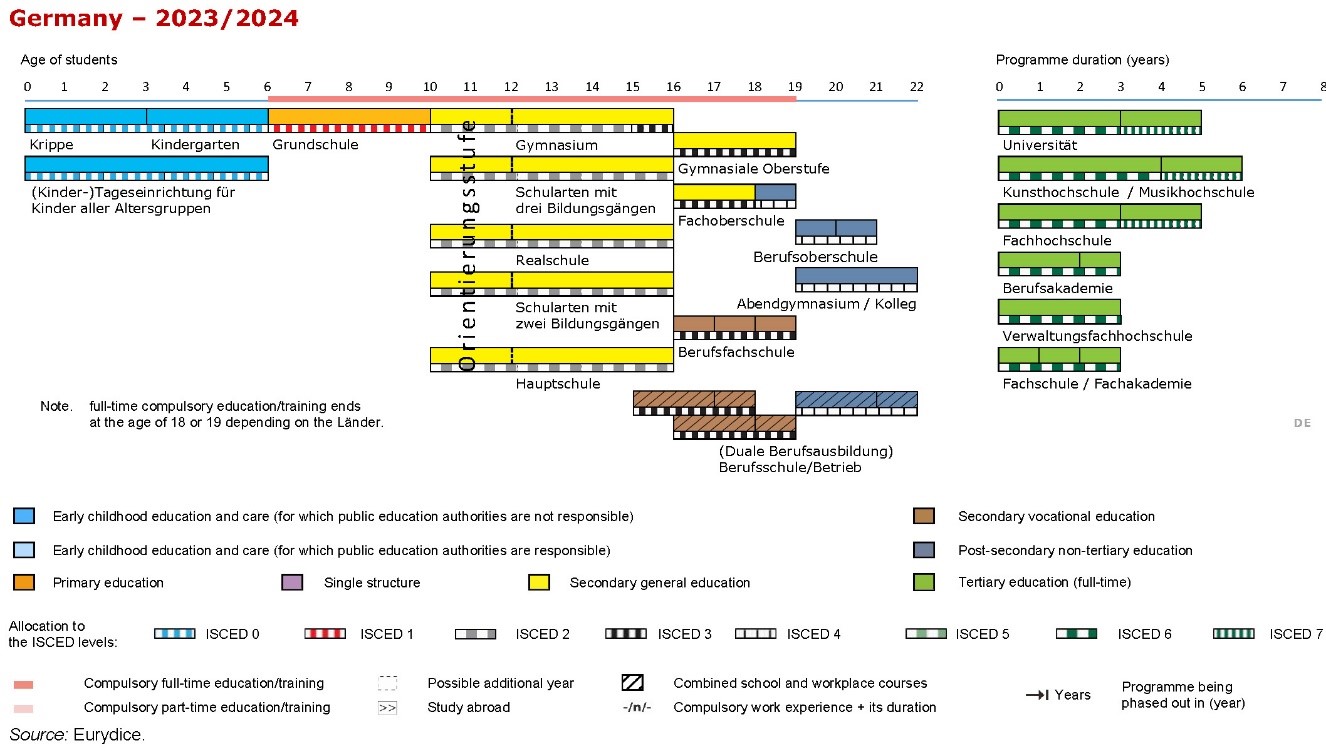
POPULAR COURSES:
- TECHNICAL
Engineering: Germany is known for its strong engineering programs, and some of the popular engineering courses are Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Computer Science. - MANAGEMENT
Business: Germany is home to some of the world’s most prestigious business schools and offers top-notch business programs such as MBA, Business Administration, and Finance. - HUMANITIES
Social Sciences: Germany has a strong tradition in social sciences, and some of the popular social science courses are Psychology, Sociology, Political Science, and Economics.
Humanities: Germany has a rich cultural heritage, and its universities offer some of the best humanities courses such as Philosophy, History, Linguistics, and Literature.
Arts: Germany is a hub of artistic and creative expression, and its universities offer world-class Arts courses such as Fine Arts, Graphic Design, and Film Studies.
- MEDICINE
Medicine: Germany has a world-renowned healthcare system and offers some of the best medical courses. Popular medical courses include Medicine, Dentistry, and Veterinary Medicine.
Universities:
Types of Universities | |
| Based on Funding | Based on Course Specialization |
| Public (TU’s and Applied Sciences) Private Religious | Universität (TU9 and other TU’s) Applied Sciences (Fachhoschschule) College of Arts and Music (Kunsthochschule and Musikhochschule) |
| UNIVERSITÄT | Applied Sciences | Private Universities | |
| They often emphasize research and theoretical foundations alongside practical applications in engineering, natural sciences, and technology. TUs usually offer a wide range of engineering programs, pure sciences, computer science, and related disciplines. | They tend to concentrate on applied sciences and practical skills, preparing students directly for specific professions or industries. UAS programs often involve internships or cooperative education arrangements with companies to provide real-world experience. | They might offer a variety of programs, including liberal arts, business, technology, and other fields. Private universities may have more flexibility in their curriculum, teaching methods, and resources due to their independence from government regulations. | |
| TU – 9 | Other Top TU’s | Top Applied Science Universities | Top Private Universities |
|
|
|
|
Intakes
In Germany, the intake periods, names, and application timelines can vary among universities and programs. However, there are generally two main intake periods:
| Intakes | Application Deadlines |
| Winter Intake (September/October) | April/May – May/July |
| Summer Intake (April) | Nov/Dec – Jan/Feb |
Winter Semester:
- Intake Name: Winter semester
- Intake Month: October
- Application Start Date: Typically starts around April or May, but it can vary by university and program.
- Application Deadline: Usually between May and July, but again, this varies based on the institution.
Summer Semester:
- Intake Name: Summer semester
- Intake Month: April
- Application Start Date: Application periods for the summer semester are shorter and less common, often starting around November or December.
- Application Deadline: Generally between January and February, but this also varies widely depending on the university.
Note:
- Some programs might have only one intake per year, usually the winter semester.
- Deadlines and start dates can vary, so it’s crucial for international students to check the specific university and program websites for accurate and updated information.
- Different universities may have different deadlines even within the same intake period.
- It’s recommended to directly contact the respective universities or visit their official websites to get precise and updated information about their intake names, months, application start dates, and deadlines.
| Medium of Instructions | Description | Requirement |
| German | In Germany, courses in German and English cater to students seeking language skills and a global outlook. Bilingual programs cover various subjects, enhancing employability. German-taught courses focus on native language and culture, while English-taught programs offer a global academic environment. Both options serve diverse educational and career goals, offering students ample opportunities for growth. | German: Showcase your command of the German language with German language proficiency test. Basic : A1, A2, Intermediate: B1, B2.1 , , B2.2 ,Professional C1, C2 or corresponding courses.
|
| English | English-taught courses are classes taught entirely in English, intended for students fluent in the language. They’re gaining popularity worldwide, offering a chance to learn in a global setting and enhance language abilities. These courses are structured to be conducted solely in English, enabling students to immerse themselves in an English-speaking academic environment, fostering both language proficiency and a broader cultural understanding. | English: Demonstrate your English proficiency with IELTS, TOEFL, or PTE etc test scores as your linguistic passport.
|
| Bilingual | German universities offer bilingual courses in both German and English, helping students improve language skills and global cultural awareness across fields like business and engineering. These programs enhance employability by fostering proficiency in both languages. German-taught courses focus on native language and culture in German-speaking regions, while English-taught courses create a global learning environment, refining English skills. Both options cater to diverse educational and career objectives, expanding opportunities for academic and professional growth. | Bilingual: For the multilingual courses/university, meet the challenge with proficiency tests in both English and German.
|
COURSES, TUITION FEE, DURATION AND ENTRY REQUIREMENTS:
| COURSES | TUTION FEE | DURATION | ENTRY REQUIREMENTS | ECTS |
| Studienkolleg | In public Studienkollegs, there’s no tuition fee, just an administrative cost of €100-€400 per semester. Private institutions, however, can charge well over €1,000 per semester. Check fees before deciding where to study. | 1 Year | Higher secondary or Diploma or equivalent qualification | —— |
| FIRST CYCLE (Bachelors/Undergraduate) | No tution fee for public universities, except for semester contribution of 250-300 Euro. Private universities Tuition Fee starts from 8,000. | 3 Year – 6 SEM3.5 Years – 7 SEM4 Year – 8 SEM | For students from these countries, the APS certificate is a prerequisite for applying to a German university. It serves as authentication for academic documents and sets eligibility criteria guiding German universities in offering admission to candidates. | 180 -240 |
| SECOND CYCLE (Masters / Graduate / Postgrad) | 1 YEAR – 2 SEM1.5 YEAR – 3 SEM2 YEAR – 4 SEM | A first academic degree that is equivalent to a bachelor’s degree in Germany. Often, the first academic degree needs to be related to the subject of the master’s degree. All info is here! | 90 -120 | |
| Third Cycle / Doctorate / PhD | Free/varies | 3 -5 Year | A scientific master’s degree, often with good grades. | —– |
| Outside Cycle (Diplom) | Free/Varies | 2 – 4 Years | Varies (often similar to bachelor’s entry requirements) | —— |
ECTS:
The ECTS system in Germany simplifies credit transfer between universities, enabling seamless transitions and international mobility for students. Undergraduate and master’s programs operate on this framework, measuring workload in credits. Bachelor’s degrees take 3 to 4 years (180-240 ECTS), including core courses, electives, practical training, and a thesis. Master’s programs last 1 to 2 years (60-120 ECTS), focusing on specialized coursework, research, and a thesis. ECTS credits provide transparency and facilitate global recognition of academic achievements, aiding students in planning and studying abroad.
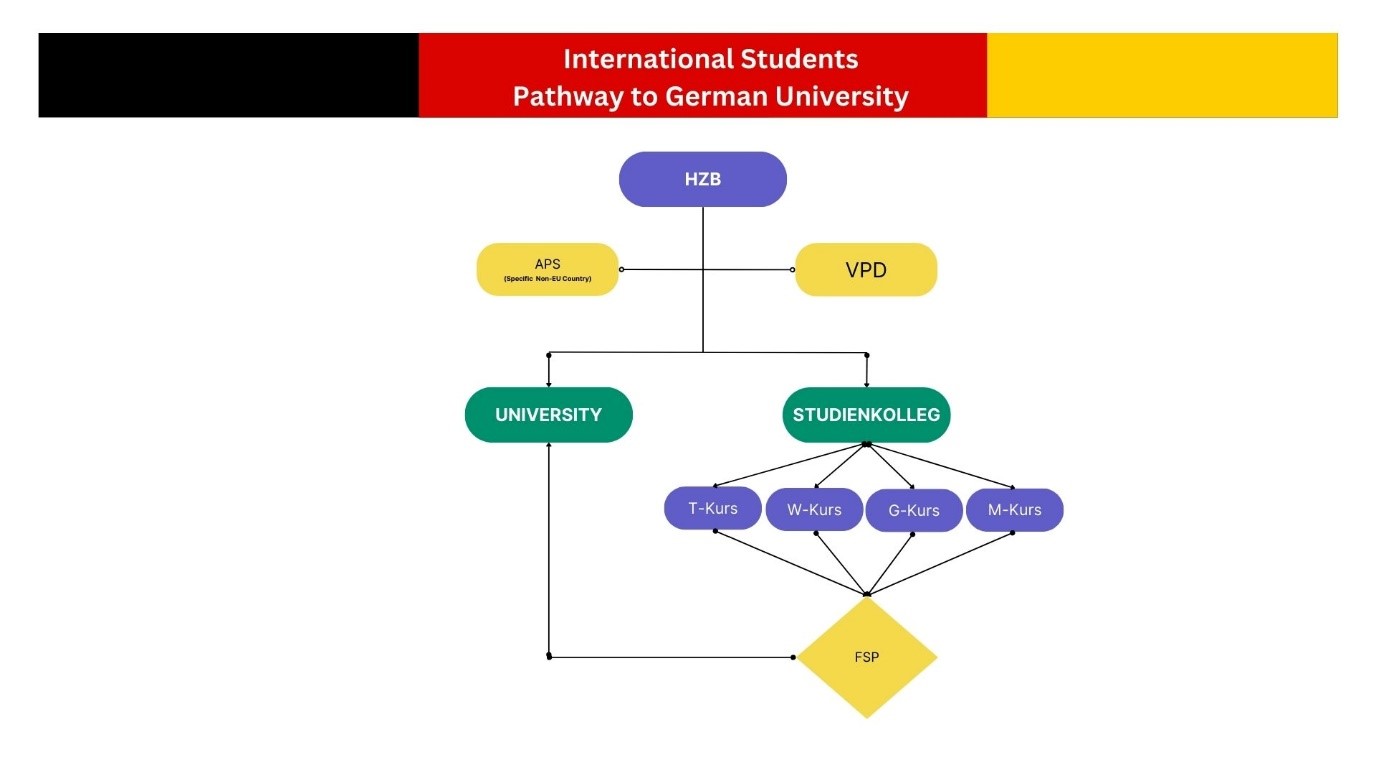
HZB
“In order to pursue studies at a German higher education institution, possessing a ‘Hochschulzugangsberechtigung’ (HZB) or university entrance qualification is mandatory. This certification, a school-leaving credential, validates eligibility for university-level education.
HZB stands as the fundamental criterion for admission to universities or colleges in Germany. It encapsulates the academic prerequisites essential for enrollment in various undergraduate programs at these institutions.
For Indian students aspiring to pursue bachelor’s programs in Germany, meeting HZB requirements is pivotal. As Germany typically requires a higher secondary qualification equivalent to 13 years of education, Indian students, who follow a 10+2 education system, can bridge this gap through preparatory courses like a Studienkolleg program, standardized tests such as the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE), or completing at least one year of a bachelor’s program in India. These alternative pathways enable Indian students to fulfill the academic prerequisites necessary for higher education pursuits in Germany.”
VPD PROCESS
The VPD (Vorprüfungsdokumentation) (preliminary review documentation) is a certificate issued by uni-assist to applicants and submit to the university on behalf of the student. The VPD contains information on which educational certificates you presented to uni-assist, outlines potential university entrance possibilities based on these credentials, and how uni-assist rates your grade within the German system of grades.
VPD (Vorprüfungsdokumentation) serve as the gateway to understanding your eligibility for German university programs. For applicants, the VPD serves as a compass, guiding you through the maze of German higher education. It offers clarity on which courses or programs might be accessible to you based on your educational background. This insight helps you make informed decisions about where to direct your applications, streamlining the process and increasing your chances of successful admission.
Uni-assist takes the reins in evaluating your documents and issuing the VPD certificate. They meticulously assess the educational qualifications you present and provide a comprehensive report, aiding both applicants and German universities in understanding the equivalence of these qualifications within the German education system.
Upon receiving your VPD, you’ll gain a clear picture of your eligibility for various programs in German universities. This document empowers you with the information needed to proceed confidently with your university applications, offering insights into how your grades align with German standards.
VPD by uni-assist acts as a vital bridge, connecting international applicants with German universities. It’s not merely a certificate but a strategic tool that simplifies the application process and ensures a smoother transition into the German higher education landscape.
Studienkolleg
| Courses | Description | Eligible course at German University after completion |
| T-Kurs | Tailored for students interested in technical studies, this track covers subjects like mathematics, physics, engineering principles, and other technical fields. It prepares students for engineering and technology-related degrees at German universities. | Ø EngineeringØ Civil EngineeringØ Automotive EngineeringØ Electrical EngineeringØ MathematicsØ PhysicsØ Business InformaticsØ Industrial EngineeringØ Industry and Processing Technology etc. |
| W-Kurs | This course is tailored for students intending to pursue degrees in economics or business-related fields. It covers subjects such as economics, finance, accounting, business administration, and related disciplines. | Ø Business StudiesØ Business Informatics/Information SystemsØ EconomicsØ SociologyØ Tourism ManagementØ LawØ Political Sciences and more |
| G-Kurs | Geared towards humanities and social sciences, this course includes subjects like literature, history, philosophy, sociology, and other liberal arts disciplines. It aims to provide a foundation in these fields for further university studies. | Ø German StudiesØ Arts & DesignØ MusicØ HistoryØ JournalismØ TheologyØ LiteratureØ PhilosophyØ Law and many more |
| M-Kurs | Specifically designed for students aiming to study medicine, this track covers subjects such as biology, chemistry, anatomy, and other sciences pertinent to medical studies. It ensures a solid foundation for students intending to pursue medical degrees in Germany. | Ø MedicineØ DentistryØ PharmacyØ BiologyØ BiochemistryØ Microbiology and more |
These courses are required because the educational systems in different countries might have varying curricula and levels of preparation for university studies. The Studienkolleg courses ensure that international students have the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed in their chosen fields at a German university. They also serve to meet the academic entry requirements set by German universities, which may differ from those of other countries.
By categorizing the courses into these tracks, the Studienkolleg aims to provide a focused and tailored curriculum that best prepares students for the specific academic demands of their chosen field of study in Germany.
FSP
At the end of the Studienkolleg courses, students typically take an assessment test called the “Feststellungsprüfung” (assessment examination) based on the respective preparatory course the student attended. This exam evaluates the students’ knowledge and skills acquired during the preparatory courses and determines if they meet the academic standards required for university admission in Germany.
The specific content and structure of the Feststellungsprüfung can vary based on the course track (W, G, M, T) and the university or Studienkolleg. Generally, it includes written and oral exams in subjects relevant to the chosen course track.
For instance: The minimum marks required to pass the Feststellungsprüfung can also differ based on the university and the specific program of study. Typically, students need to achieve a passing grade in this examination to be eligible for admission to a German university.
The passing criteria might involve reaching a certain overall score or passing each section of the examination individually. Students should check the requirements set by the specific university or Studienkolleg they are aiming to attend for the most accurate and updated information regarding minimum marks or grades needed for admission.
Post Study Visa:
VISA PROCESS:
International students aiming to study in Germany undergo a visa process that typically involves these steps:
1. Apply to a German university: Admission into a German university is the initial step before applying for a student visa.
2. Gather necessary documents: Students need a passport, proof of finances, health insurance, and an acceptance letter from the university.
3. Schedule an embassy appointment: Booking an appointment at the German embassy or consulate in their home country is crucial, ideally well in advance due to potential lengthy processing times.
4. Attend the appointment: During this visit, students submit their visa application and required documents, sometimes followed by an interview.
5. Await visa processing: The processing time for the visa varies, ranging from weeks to months based on the embassy or consulate’s workload.
6. Travel to Germany: Once the visa is approved, students can travel to Germany to commence their studies.
The visa process can vary depending on individual circumstances, emphasizing the importance of students checking specific requirements and procedures with their local German embassy or consulate.
APS (Anerkennung and Bewertung ausländischer Bildungsnachweise)
The APS, managed jointly by the German Embassy and the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), is an essential step for students from select countries like China, Vietnam, and India aiming to pursue higher education in Germany. For students from these countries, the APS certificate is a prerequisite for applying to a German university. It serves as authentication for academic documents and sets eligibility criteria guiding German universities in offering admission to candidates.
The APS meticulously verifies the authenticity of educational biographies and corresponding certificates from these countries. Upon a positive assessment, it issues certificates crucial for applying to German universities.
The APS process is a crucial step for students from select countries seeking to study in Germany. Completing this process in a timely manner can significantly benefit your university application and visa process.
Holding an APS certificate streamlines your application to German universities and expedites your student visa application. This original certificate, a mandatory requirement for the student visa, demonstrates the authenticity of your academic background.
Students sponsored by German or EU-funded scholarships are exempt from the APS certification process.
To expedite the application process, it’s advisable to complete the APS process before applying to a German university. This approach helps minimize processing times for your student visa application.
The APS certificate isn’t just a formality; it’s your key to unlocking opportunities for higher education in Germany. It streamlines your application process, ensuring your academic authenticity and enhancing your chances of a smooth transition to German universities.
TOP COMPANIES










Germany is home to many world-renowned companies across various industries, including automotive, engineering, pharmaceuticals, and technology. Here are some of the top companies in Germany:
1. Volkswagen AG – Automotive
2. Siemens AG – Engineering, Electronics, and Healthcare
3. BMW Group – Automotive
4. Daimler AG – Automotive
5. BASF SE – Chemicals
6. Bayer AG – Pharmaceuticals
7. Allianz SE – Insurance and Financial Services
8. Deutsche Bank AG – Banking and Financial Services
9. SAP SE – Technology
10. Adidas AG – Sportswear and Accessories
These companies are known for their innovative products, services, and contributions to their respective industries. Many of them offer excellent career opportunities for professionals and graduates in Germany and around the world.
Average Salary
DAAD:
Deutscher Akademischer Austausch Dienst (German Academic Exchange Service)
Est: 1925, HQ: Bonn, Germany, Non – Profit Organization that promotes international academic exchange between Germany and other countries. The DAAD offer numerous programs and services to support international scholars, researchers and students;
1. Stipends
2. Research Grants
3. Language course
4. Exchange programs
Goal: To promote understanding and cooperation between Germany and other countries through education and research.
Uni-Assist:
Non – Profit of Organization that supports international students’ applicants and German Universities in processing application to study in Germany.
It is the central point of contact for international students applying to 170+ German Universities that are part of / members of Uni-Assist.
Uni-Assist Services
1. Application processing
2. Admission advice
3. Support for universities
Benefits of Uni-Assist
1. Convenience
2. Expertise
3. Speed
4. Accuracy/precision
How to Apply?
- You Apply
Tell us a little about yourself and we’ll help with the rest. Our convenient online application tool only takes 10 minutes to complete.
- We Connect
After you submit your application, an admissions representative will contact you and will help you to complete the process.
- You Get Ready
Once you’ve completed your application and connected with an admissions representative, you’re ready to create your schedule.
